

In Vivo Nitroreductase Imaging via Fluorescence and Chemical Shift Dependent F-19 NMR
Recently, Ultrasensitive Magnetic Resonance Research Group designed and constructed a dual-modal molecular probe nitro-fluoride Cy7, which realized the 19F magnetic resonance and near-infrared fluorescence accurate imaging of nitroreductase in living lung cancer. The relevant research results were published in Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., and was selected as a VIP (Very Important Paper) in this issue.
Nitroreductase (NTR) is an important biomarker widely used to evaluate tumor hypoxia. Although there are already some optical imaging methods for in vivo imaging of nitroreductase, the shortcomings such as the depth of tissue penetration and the low quantitative concentration limit its wide application in clinical diagnosis. 19F MRI can directly detect 19F nucleus signals, and there is no background signal interference in vivo imaging, and the signal intensity is proportional to the concentration of exogenous probes, which has the potential to become a complementary new technology in clinical applications of traditional 1H MRI. In this system, FCy7-NO2 can not only be used as a fast-response near-infrared fluorescence-enhanced probe for monitoring nitroreductase in lung cancer but also can be used to selectively target nitroreductase in deep lung cancer for in vivo imaging using the molecule's 19F MRI chemical shift sensitivity.
The method proposed in this work for the precise imaging and quantitative analysis of nitroreductase in tumors using 19F magnetic resonance/fluorescence dual-modal imaging technology can provide an important tool for the accurate diagnosis of tumor markers. At the same time, the content of nitroreductase can be used to distinguish between normal and hypoxic tumor tissues and quantitatively assess the degree of hypoxia, which is expected to provide new methods and technologies for the biomedical field.
The first authors of the article are professor Shizhen Chen and PhD candidate Long Xiao. The corresponding author is professor Xin Zhou.
The work was supported by the Ministry of Science and Technology, the National Natural Science Foundation of China, and the Chinese Academy of Sciences.
Link to paper: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/anie.202213495
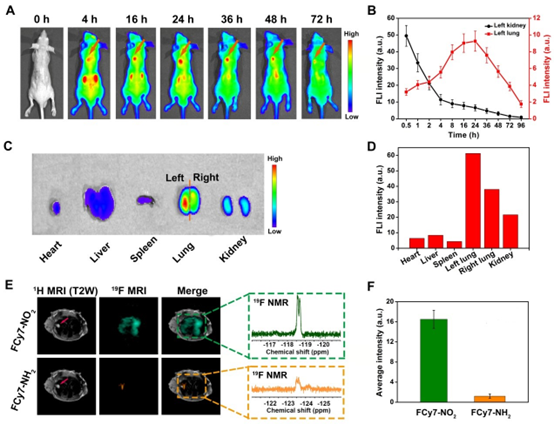
FCy7-NO2 can identify lung cancer in situ with near-infrared fluorescence and 19F MR chemical shift imaging

Very Important Paper

Innovation Academy for Precision Measurement Science and Technology, CAS.
West No.30 Xiao Hong Shan, Wuhan 430071 China
Tel:+86-27-8719-8631 Fax:+86-27-8719-9291
Email:hanyeqing@wipm.ac.cn
鄂ICP备15017570号-1